Quick Start
To understand how Redis Cache Java works, it’s best to try it for yourself.
This example showcases a Spring Boot application using Redis Cache Java.
Prerequisites
-
Java 17 or later
-
Docker and Docker Compose
-
Git
-
API token from themoviedb.org
Installation
First, clone the git repository:
git clone https://github.com/redis-field-engineering/redis-cache-java-dist.git
cd redis-cache-java-distNext, register and create an API read-access token at themoviedb.org.
Set the following environment variable with the token:
export TMDB_TOKEN=<your API read-access token>Running the Demo
Use Docker Compose to launch containers for Redis, Prometheus and Grafana:
docker compose upFinally, launch the demo app with this command:
./gradlew bootRunExploring the Demo
You can access the demo at http://localhost:8080.
As you click around on the different pages, notice how the response time improves after the first time you request a page.
Open another browser window and access the Grafana dashboard.
Use username/password admin/admin to log in.
You can skip changing password.
Arrange your browser windows with the demo app on the left and Grafana on the right:
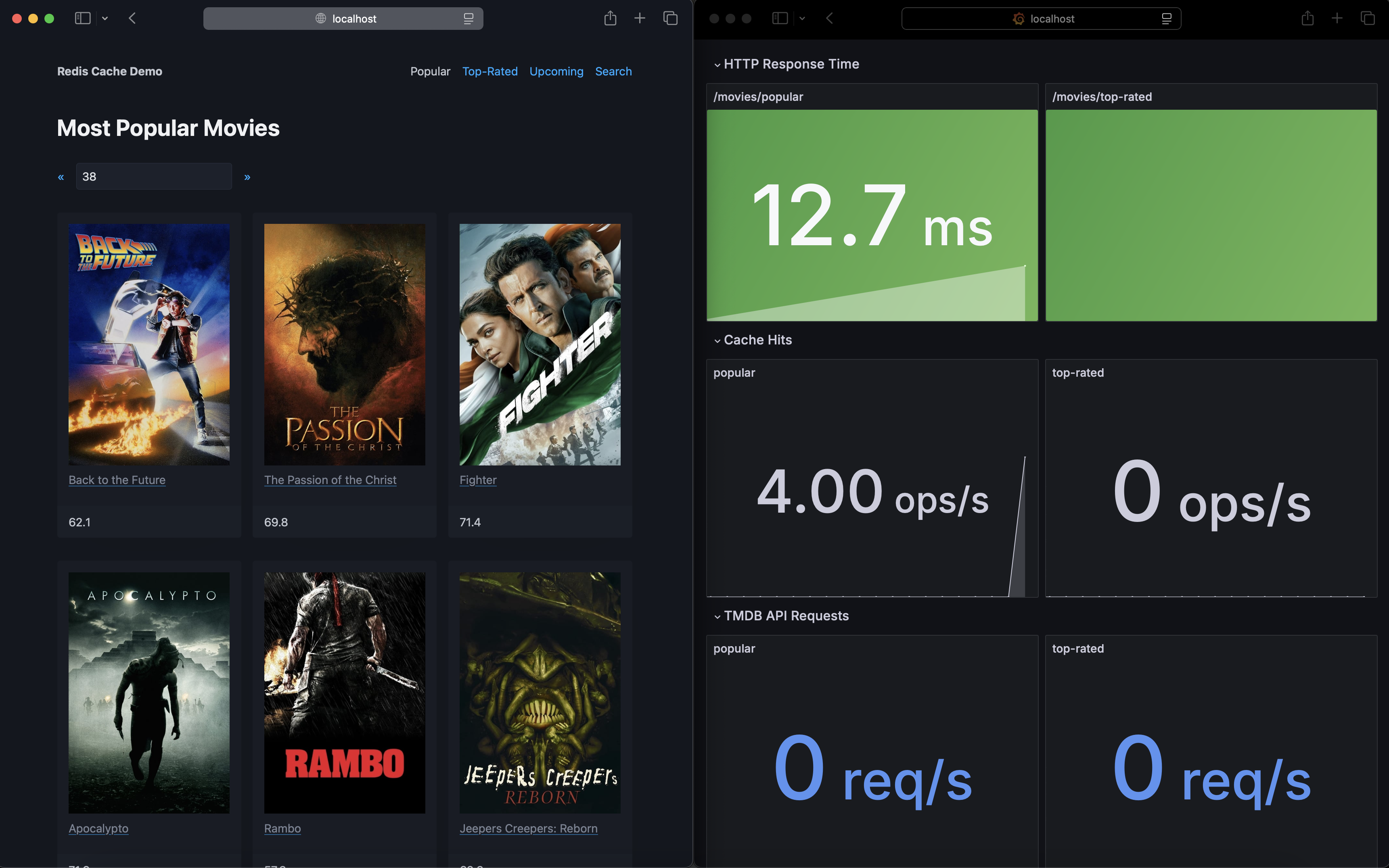
Notice the HTTP response time decreasing with cache hits, and increasing with API requests.
Search Feature
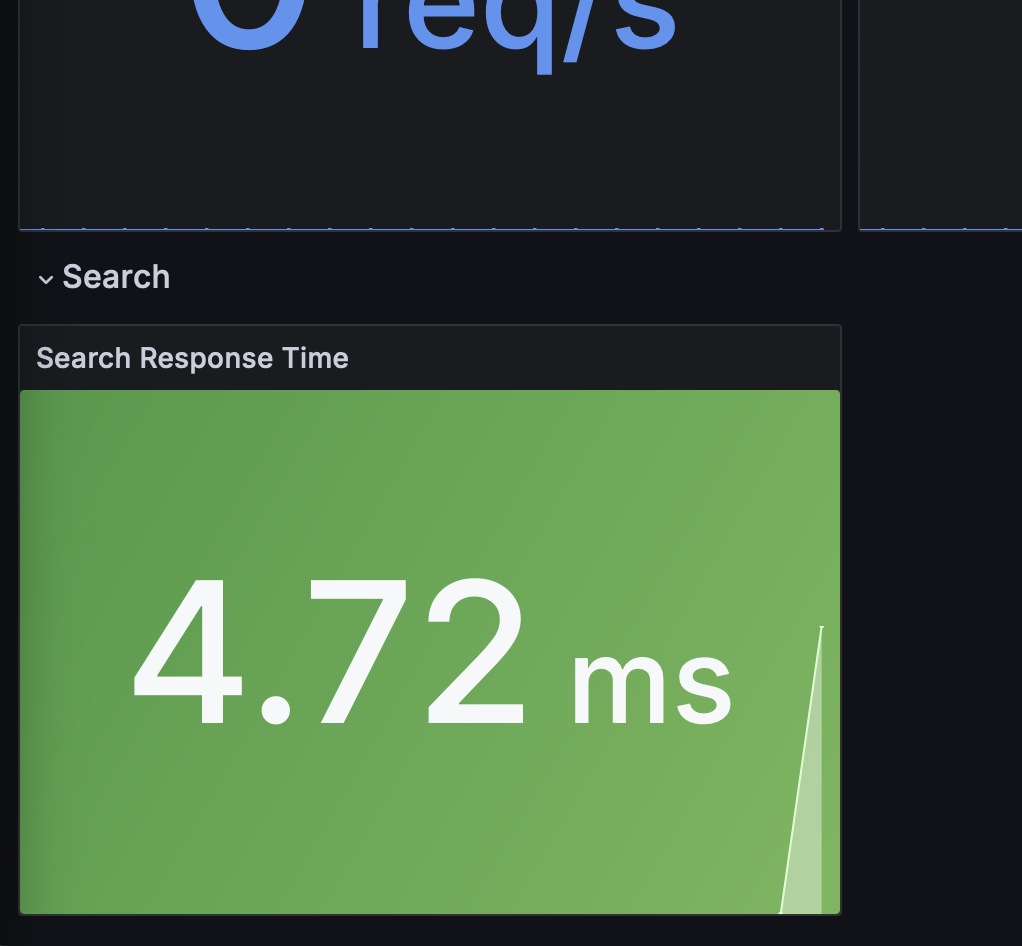
Now click on the Search link to search the cache, for example with keyword corleone.
Notice how quickly search results are returned: the search feature is powered by Redis.
Search response time can be visualized with the panel at the bottom of the Grafana dashboard.
Next Steps
Now that you’ve seen Redis Cache Java in action, learn how to integrate it into your own application:
-
Usage Guide - Learn how to add Redis Cache Java to your project
-
Configuration - Explore configuration options
-
Features - Discover advanced features like indexing and async mode

